1、Initialization parameter
Before wiring, initialize the parameters.
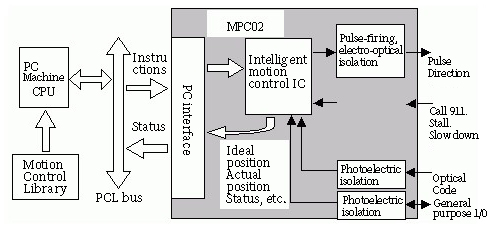
On the control card: select the control mode; Set PID parameters to zero; Let the control card power on by default enable signal off; Save this state to ensure that it is there when the control card is powered up again.
On the servo motor: set the control mode; Setting enables external control; Gear ratio of encoder signal output; Set the proportional relationship between the control signal and the motor speed. In general, it is recommended to make the maximum design speed in the servo operation correspond to 9V control voltage. Panasonic, for example, sets the speed to a voltage of 1V with a factory value of 500. If you are only going to make the motor work at less than 1000 rotations, set this to 111.
2、wiring
Disconnect the control card and connect the signal line between the control card and the servo. The following lines must be connected: analog output line of control card, enabling signal line, servo output encoder signal line. The motor and control card (as well as the PC) will be powered on after rechecking the wiring and there is no error. The motor should be stationary and can be easily rotated by external forces. If not, check the setting and wiring of enabling signals. Rotate the motor with external force, check whether the control card can correctly detect the change of motor position, otherwise check the wiring and setting of the encoder signal.
3、Try the direction
For a closed-loop control system, if the feedback signal is not directed in the right direction, the consequences can be catastrophic. Enable the servo signal through the control card. This is where the servo should turn at a lower speed, known as 'zero drift'. Generally, there are instructions or parameters on the control card to suppress zero drift. Use this command or parameter to see if the speed and direction of the motor can be controlled by this command (parameter). If not, check analog wiring and parameter Settings for control mode. Confirm that a positive number is given, the motor is turning forward, and the encoder count is increased; The negative number is given, the motor rotates backwards, and the count of the encoder decreases. Do not use this method if the motor is loaded and has limited travel. Test not to give too much voltage, recommended below 1V. If the direction is inconsistent, you can modify the parameters on the control card or motor to make them consistent.

4、Inhibition of zero drift
In the closed-loop control process, zero drift will have a certain influence on the control effect, and it is best to suppress it. Using the control card or servo to suppress the zero drift parameters, carefully adjust, so that the motor speed tends to zero. Because zero drift itself also has a certain randomness, so it is not necessary to require the motor speed to be absolutely zero.
5、Establish closed loop control
Again, the servo enabling signal is released through the control card, and a small proportional gain is input on the control card, which can only be felt by the senses. If you are really worried, input the minimum value allowed by the control card. Turn on the enable signals for the control card and servo. At this point, the motor should be able to move roughly in accordance with the motion instructions.
6、Adjust the closed-loop parameters
Fine-tune the control parameters to ensure that the motor moves in accordance with the command of the control card, which is a must work, but this part of work, more experience, here can only be a brief.